This fall I am volunteering as a Peer Group Leader for the Research Like a Pro Study Group hosted by Diana Elder and Nicole Dyer of Family Locket. Making the transition from family historian to professional genealogist required me to become a more disciplined researcher. The team at Family Locket supported me on my journey through their podcast, books, courses, and presentations at conferences. I’m a process person likely due to my background in quality improvement. Throughout my healthcare career, the Model for Improvement guided our efforts with the message “Every system is perfectly designed to get the results it gets.” (Paul Batalden, often quoted by Don Berwick). To improve as a genealogist, I needed to change my system. In this case, that’s the research process. For the next ten weeks, I will share my insights into the Research Like a Pro process. This course is focusing on documentary research. As a peer group leader, I will be completing a project with the participants. It’s a great opportunity to work on my own family history.
Pedigree Analysis
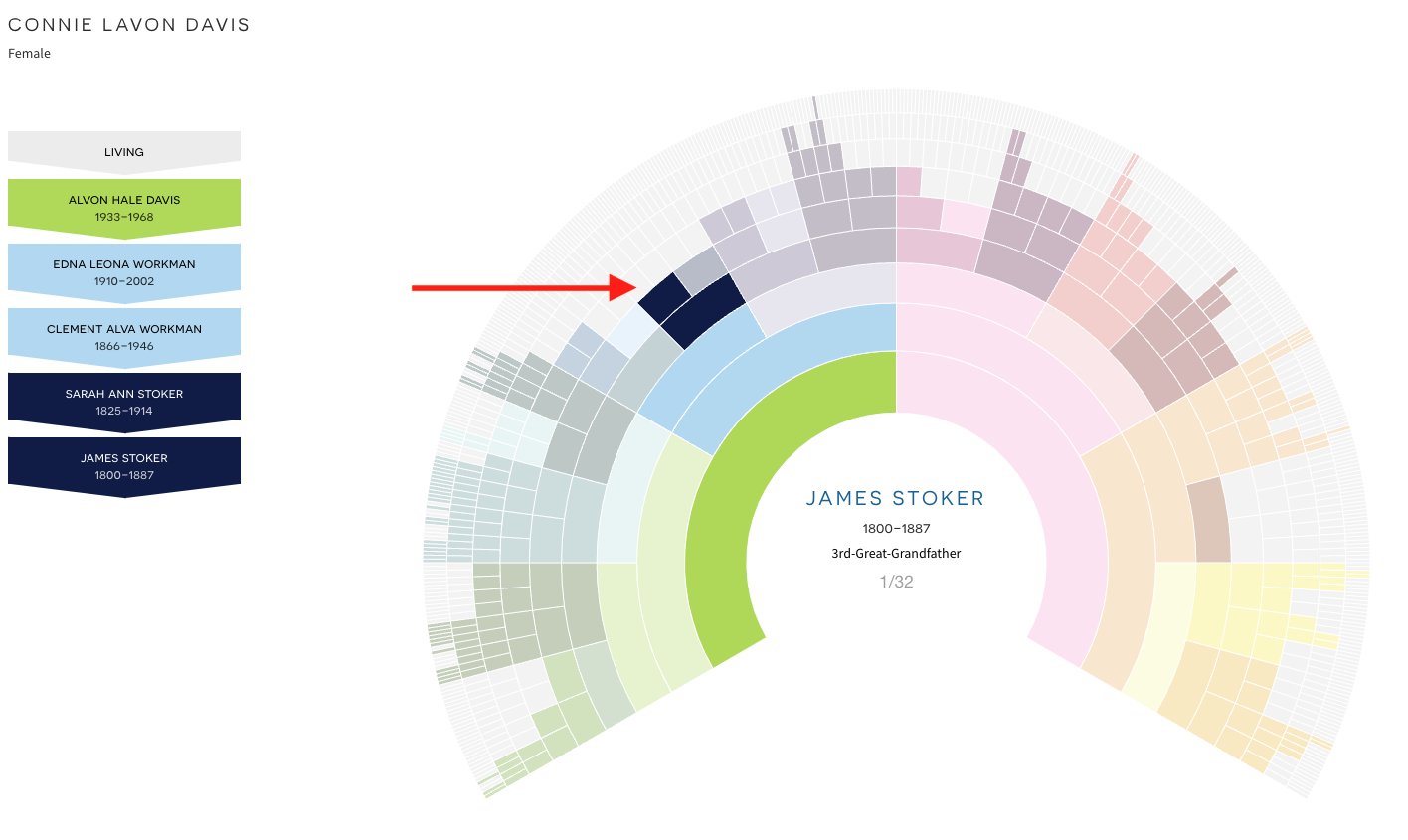
Identifying potential areas for research is the first step in making the most of your research efforts. Analyzing your pedigree accomplishes this step. DNA Painter provides multiple ways to visualize your family tree. The first thing I checked was my tree completeness. This tells me where I have gaps in my tree and also reminds me about pedigree collapse, which is a subject for a different blog.
I’m missing two 3x-great grandparents and sixteen 4x-great grandparents. A fan chart, like this example from DNA Painter is another way to look at the gaps. On DNA painter, hovering over each colored shape brings up the name of the person represented in that space on the chart. That feature isn’t shown in the image below since I can’t capture the hovering. You can use this link to see it for yourself. My father’s side of the family is on the left and my mother on the right. I’ve coordinated these colours to resemble the coloured dots I use on Ancestry to mark my DNA matches.
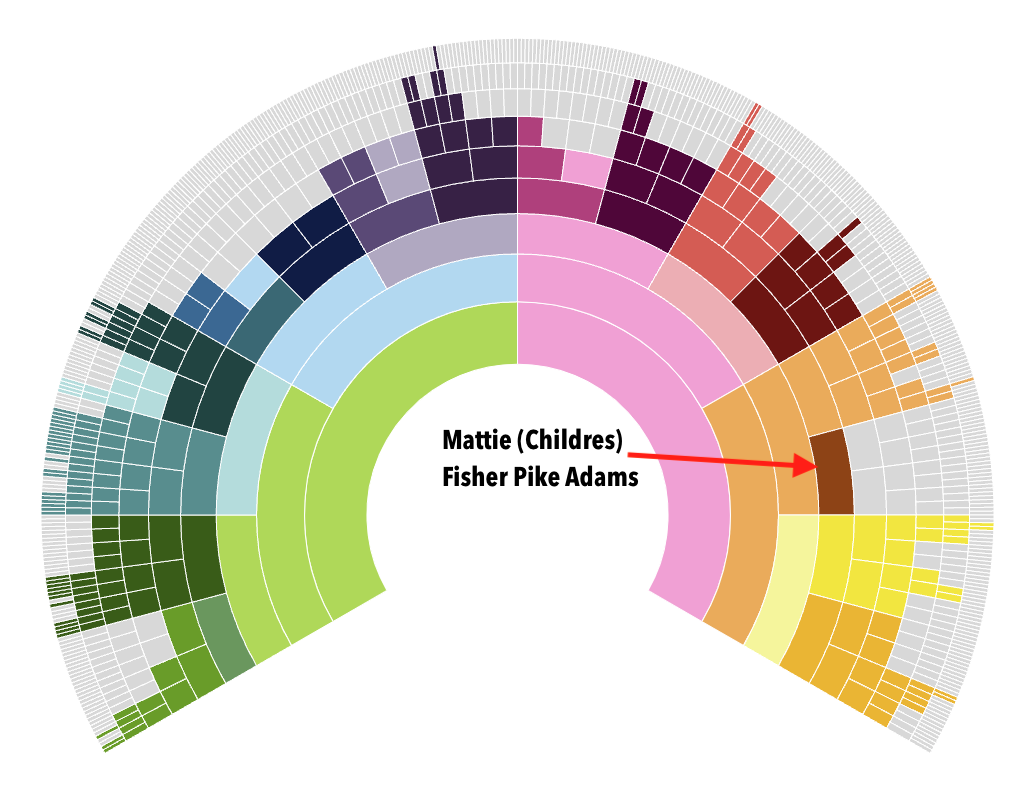
The arrow indicates the location of the most recent ancestor whose parents I don’t know. Many refer to this as a “Brick Wall.” I could continue documentary research on Mattie for this course. During the Research Like a Pro with DNA e-course I completed, I identified several families that could be Mattie’s parents.
Another opportunity is my 3x-great grandfather, James Stoker, shown below.
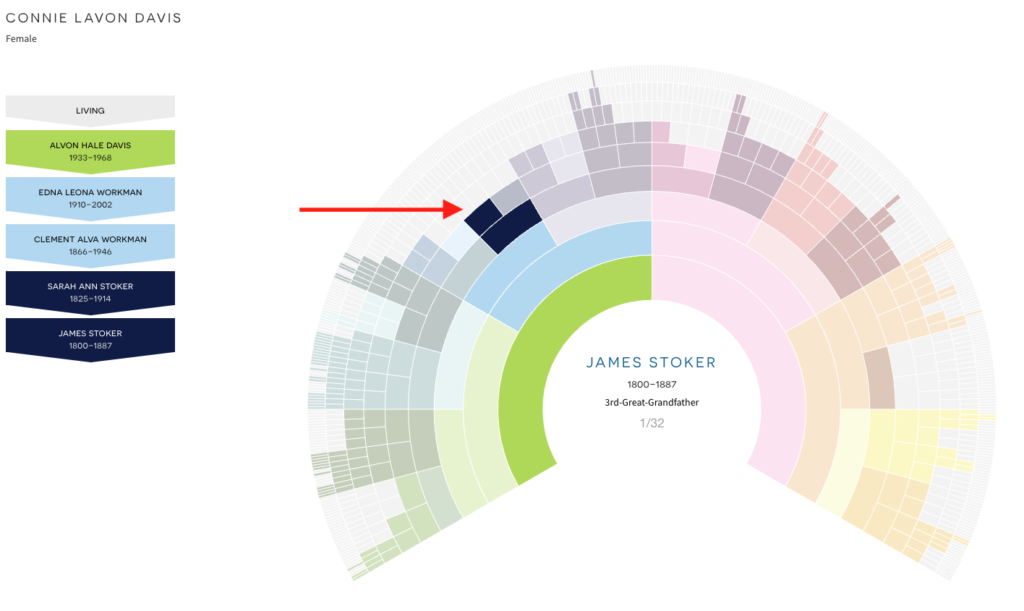
My grandmother believed he was the son of Edward Stoker, a Revolutionary War Veteran. During ProGen 46, I took a look at the link between generations from Edward Stoker to my 3x-great grandfather James and realized there were multiple men named James Stoker who could have been his son James, as noted in a Stoker family Bible. Several of them left records in Bourbon County, Kentucky around 1820 where my ancestor James Stoker married Polly Ross on 9 December 1822. I also noted that the birth date of James Stoker in the family Bible of Edward Stoker (found in his Revolutionary War Pension file) did not match the birthdate of my 3x-great grandfather. Many family trees shared on Ancestry confuse the James Stokers, and the Ancestry hinting algorithm points to Edward Stoker. WikiTree has my James Stoker linked to Edward. The FamilySearch Family Tree has a note about the confusion: ” Be aware…. Another Individual, ‘James T Stoker’ was born in Kentucky and resided most of his live [sic] in Nicholas County, KY. Married Sytha Ann McDonald 20 Dec 1827 in Nicholas Co KY.” I didn’t fully analyze the same-name people when I first discovered the confusion. Thoroughly researching the men and writing up the results would be a contribution and help me correct the WikiTree entry.
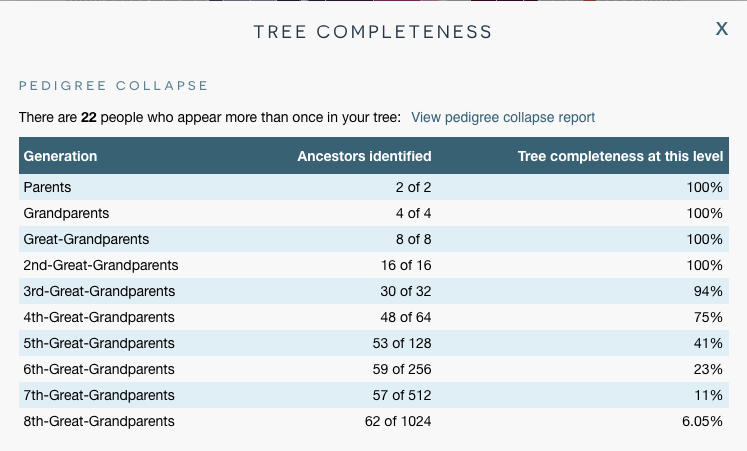
Another way of analyzing my pedigree and determining where I could focus is using Yvette Hoitink’s Level Up Challenge. I started working on improving my genealogy based on her approach after she published this idea in her blog in January of 2021. The levels describe the completeness of your research for each ancestor. In some cases I’m not sure which level to give because I write a biography for everyone on WikiTree. I may not have researched all property records (some parts of my family were very mobile) or know every church denomination they attended over time. I used DNA Painter’s Dimensions “Research Level” feature to create this chart.
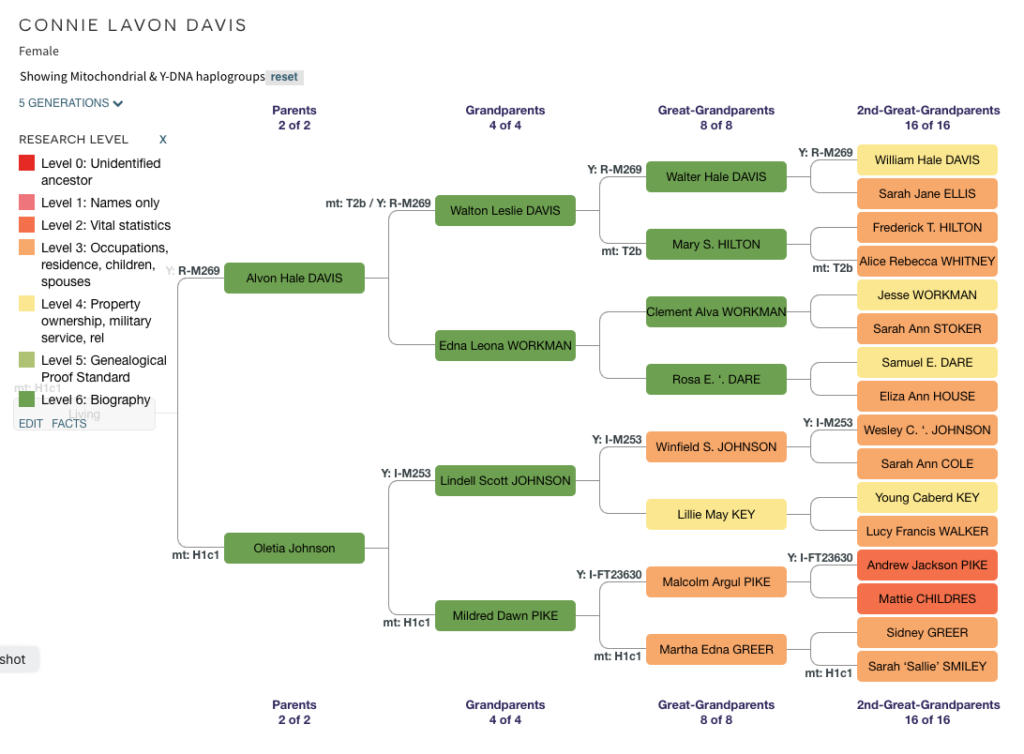
Based on this diagram, my efforts would be to continue researching my mother’s family, particularly Andrew Jackson Pike and Mattie Childres that I designated as Level 2. (Note: See the YDNA and mtDNA haplogroups? That’s a neat feature of the tree on DNA Painter, and another project is to complete my YDNA and mtDNA tree like Roberta Estes does). I spend a lot of time researching my mother’s family and have neglected my paternal grandmother’s family including James Stoker.
I haven’t written up a same-name case before, so that’s my choice for this project. I expect that writing clearly will be the biggest challenge. For reference, I have two National Genealogical Society (NGSQ) articles I reviewed during my NGSQ Study Group. One is by Shannon Green, who was my mentor in ProGen 46. The other is by Allen R. Peterson and Stephen J. Allen. Both are found in the December 2019 NGSQ
File Organization
Our assignment this week also asks us to describe how we name and organize files and how our choices support our research.
I organize documents in two ways depending on where I am in the research process. My basic family history files structure relies on folders for the surnames of each of my sixteen 2x-great grandparents. Within those folders there are sub-folders for individuals. Women are filed under their maiden name, since it is the only constant. While I am working on a specific project, I create a project folder within the surname or person. Project folders start with a number like 01-Mattie Childres Father so that it will sort at the top. Within each project folder, there is a sources folder.
I use the following naming conventions for files (.jpg, .pdf, .docx, etc.) so that the folder becomes a timeline:
YYYY-MM-DD_LASTNAME_Firstname_Middleifpresent_STATE_County_Town_type.file
- Dates: YYYY-MM-DD format keeps them sorted. I include as much detail as I have. It could be year only, year and month, or all three. If I don’t have the exact date, I use the best information I have and put “ca” after the date so I know it is approximate and the sorting order is maintained.
- Names are written as they appear in the record with the surname in ALL CAPS. The caps help me scan the files for surnames and variations.
- State is the two-digit state or province abbreviation.
- Type is the type of document
- File is the extension (pdf, jpg, docx).
Examples:
1840_STOKER_Jas_KY_Bourbon_census.jpg
1882-11_SMILEY_James_KY_Floyd_court.jpg
1955ca_DAVIS_Alvon_AK_Kodiak_letter_to_DAVIS_Edna_transcription.docx
When I complete a project or identify a document I know I want to cite in Reunion (family tree software for Mac) I make a duplicate and add the source number that Reunion assigns to the beginning of the name and file it in a a digital folder in my Reunion folder.
Filed in Reunion:
2622-1882_11_SMILEY_James_KY_Floyd_court.jpg
I keep any useful paper copies in plastic sleeves in 3 ring binders in numeric order of the Reunion citation. I should invest in some archival safe plastic sleeves for the few originals that I own.
Research Objective
A possible research objective is:
The goal of this project is to identify which of multiple James Stokers known to have been in Kentucky was the son of Edward Stoker. Edward Stoker served in Capt. John Lemon’s Company during the Revolutionary War and died 7 May 1846 in Nicholas County, Kentucky.
Another option is:
The goal of this research project is to clarify the identities of men named James Stoker in Bourbon County, Kentucky from approximately 1820 to 1840. James Stoker filed a bond to marry Polly Ross on 9 December 1822 in Bourbon County. Jas. Stoker, age 79, lived in the household of his son-in-law, Jas. Cleaver, in 1880 in Millersburg, Bourbon County. James H. Stoker, presumed age 40-50, lived in Bourbon County in 1830.
I have additional information about the men named James Stoker in Kentucky but I think it would confuse the objective. I can put it in the next section of my research project document, summary of known facts. The objective identifies Edward Stoker, because I realize he is the person I can identify at present. I look forward to receiving feedback from my coursemates!